Shared Interest...Sometimes: Understanding the Alignment between Human Perception, Vision Architectures, and Saliency Map Techniques
Abstract
Empirical studies have shown that attention-based architectures outperform
traditional convolutional neural networks (CNN) in terms of accuracy and
robustness. As a result, attention-based architectures are increasingly used in
high-stakes domains such as radiology and wildlife conservation to aid in
decision-making. However, under- standing how attention-based architectures
compare to CNNs regarding alignment with human perception is still
under-explored. Previous studies exploring how vision architectures align with
human perception evaluate a single architecture with multiple explainability
techniques or multiple architectures with a single explainability tech- nique.
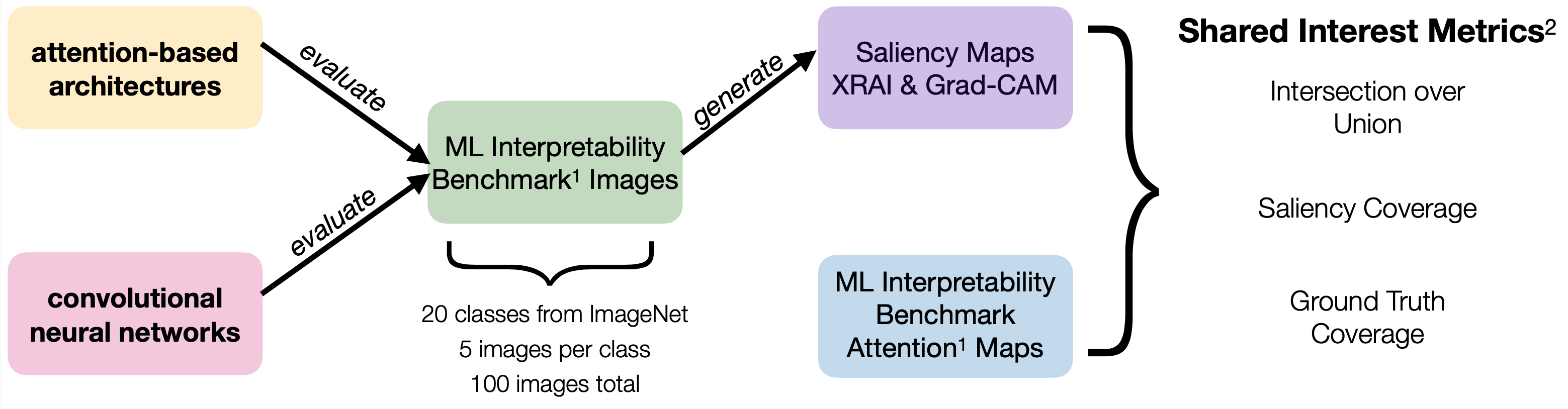
Through an empirical analysis, we investigate how two attention-based
architectures and two CNNs for two saliency map techniques align with the ground
truth for human perception on 100 images from an interpretability benchmark
dataset. Using the Shared Interest metrics, we found that CNNs align more with
human perception when using the XRAI saliency map technique. However, we found
the opposite for Grad-CAM. We discuss the implications of our analysis for
human-centered explainable AI and intro- duce directions for future work.